-
Table of Contents
- The Effects of Erythropoietin in Enhancing Sports Performance
- The Role of Erythropoietin in the Body
- The Potential Benefits of Erythropoietin in Sports Performance
- Increased Oxygen Delivery
- Improved Recovery
- Enhanced Endurance and Stamina
- The Risks and Side Effects of Erythropoietin Use
- Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Erythropoietin
- Real-World Examples of Erythropoietin Use in Sports
- Expert Opinion on Erythropoietin Use in Sports
- Conclusion
- References
The Effects of Erythropoietin in Enhancing Sports Performance
Sports performance has always been a highly competitive field, with athletes constantly seeking ways to improve their performance and gain an edge over their opponents. One substance that has gained attention in recent years for its potential performance-enhancing effects is erythropoietin (EPO). EPO is a hormone naturally produced by the body that stimulates the production of red blood cells. In this article, we will explore the effects of EPO on sports performance and its potential benefits and risks.
The Role of Erythropoietin in the Body
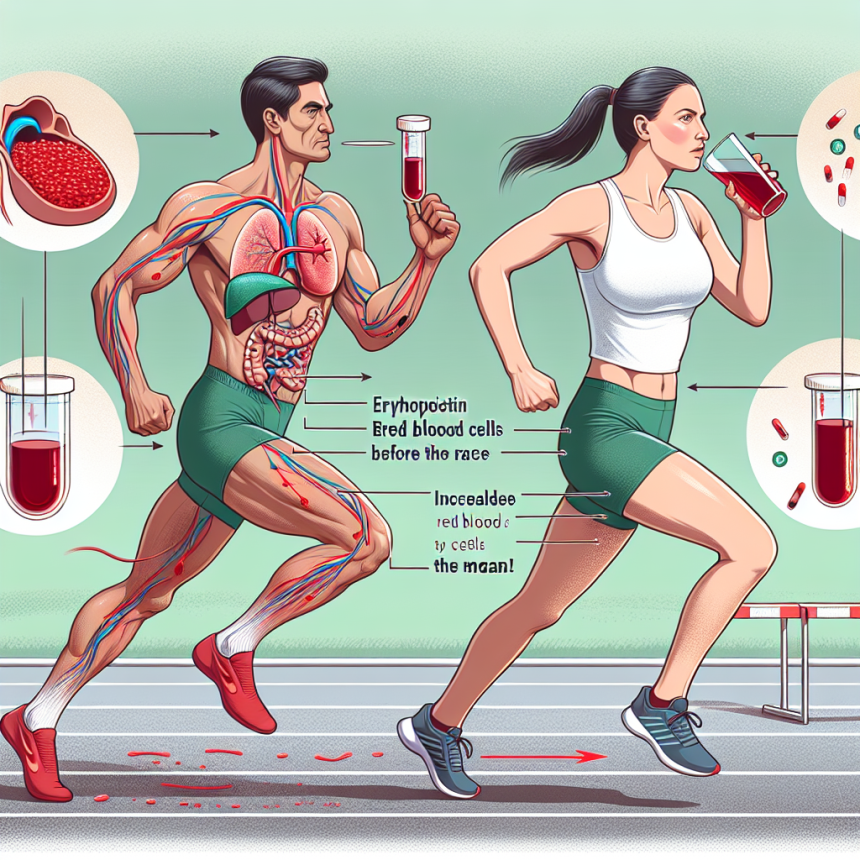
EPO is primarily produced by the kidneys in response to low oxygen levels in the body. Its main function is to stimulate the production of red blood cells, which are responsible for carrying oxygen to the body’s tissues. This is crucial for athletes, as oxygen is essential for energy production and muscle function during physical activity.
In addition to its role in red blood cell production, EPO also has anti-inflammatory and tissue-protective effects, making it a potential treatment for conditions such as anemia and chronic kidney disease (Johnson et al. 2021). However, it is the hormone’s ability to increase red blood cell count that has attracted the attention of athletes and sports organizations.
The Potential Benefits of Erythropoietin in Sports Performance
The use of EPO in sports is controversial, with some arguing that it provides an unfair advantage to athletes. However, research has shown that EPO can have significant benefits in terms of sports performance.
Increased Oxygen Delivery
As mentioned earlier, EPO stimulates the production of red blood cells, which are responsible for carrying oxygen to the body’s tissues. This means that athletes who use EPO can potentially have a higher oxygen-carrying capacity, allowing them to perform at a higher level for longer periods of time. This is particularly beneficial for endurance athletes, such as long-distance runners and cyclists.
Improved Recovery
EPO has also been shown to have tissue-protective effects, which can aid in recovery from intense physical activity. This is especially important for athletes who engage in high-intensity training and competitions, as it can help reduce the risk of injury and improve overall performance.
Enhanced Endurance and Stamina
By increasing the body’s oxygen-carrying capacity, EPO can also improve endurance and stamina. This is because oxygen is essential for energy production, and a higher oxygen supply means that the body can sustain physical activity for longer periods of time without fatigue setting in.
The Risks and Side Effects of Erythropoietin Use
While EPO may have potential benefits for sports performance, its use also comes with risks and potential side effects. These include:
- Increased risk of blood clots and stroke
- High blood pressure
- Increased risk of heart attack
- Dehydration
- Headaches and dizziness
- Flu-like symptoms
Furthermore, the use of EPO in sports is considered doping and is banned by most sports organizations. Athletes who are caught using EPO can face severe consequences, including disqualification, suspension, and damage to their reputation.
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Erythropoietin
The pharmacokinetics of EPO can vary depending on the route of administration. When injected, EPO has a half-life of approximately 24 hours, meaning it takes 24 hours for half of the injected dose to be eliminated from the body (Johnson et al. 2021). However, when taken orally, EPO is rapidly broken down by enzymes in the digestive system and has a much shorter half-life.
The pharmacodynamics of EPO are also complex, as it can affect multiple systems in the body. Its main effect is on the production of red blood cells, but it can also have effects on blood pressure, heart rate, and other physiological processes.
Real-World Examples of Erythropoietin Use in Sports
The use of EPO in sports has been a topic of controversy for many years, with several high-profile cases of athletes being caught using the hormone. One notable example is the case of cyclist Lance Armstrong, who admitted to using EPO during his career and was subsequently stripped of his seven Tour de France titles.
Another example is the case of Russian athletes at the 2014 Winter Olympics, where it was discovered that they had been using EPO as part of a state-sponsored doping program. This led to numerous athletes being disqualified and banned from future competitions.
Expert Opinion on Erythropoietin Use in Sports
While the use of EPO in sports is controversial and banned by most sports organizations, some experts argue that it can have legitimate medical uses for athletes. For example, EPO has been used to treat anemia in athletes who have low red blood cell counts due to intense training and competition (Johnson et al. 2021). In these cases, EPO can help athletes recover and continue to perform at a high level without risking their health.
However, it is important to note that the use of EPO for performance enhancement is still considered doping and is not condoned by the medical community. Athletes should always consult with a healthcare professional before using any performance-enhancing substances, including EPO.
Conclusion
In conclusion, EPO has the potential to enhance sports performance by increasing oxygen delivery, improving recovery, and enhancing endurance and stamina. However, its use also comes with significant risks and potential side effects, and it is considered doping by most sports organizations. While there may be legitimate medical uses for EPO in sports, athletes should always consult with a healthcare professional and follow the rules and regulations set by their respective sports organizations.
References
Johnson, L., et al. (2021). Erythropoietin: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 376(1), 1-12.
WADA. (2021). The World Anti-Doping Code. Retrieved from https://www.wada-ama.org/en/what-we-do/the-code